What causes periodontitis in children?
Periodontitis, an advanced stage of gum disease, is a common condition among adults. However, a number of factors can lead to this oral health problem in the youngest members of the family. Gum disease can destroy the tissues that support teeth, even if they are baby teeth. Since gum health is as important as tooth health, it is important to know what periodontal disease in children is and how to prevent it.
What you need to know to prevent periodontitis in children.
- What is periodontitis in children?
- Why does periodontitis appear?
- How can we detect it in children?
- Can periodontitis in children be prevented?
- What is periodontal treatment like?
1. What is periodontitis in children?
As in adults, periodontitis in children is a severe inflammatory bacterial infection. It is the result of untreated gingivitis. A periodontal disease that progressively destroys the supporting tissues of the teeth, even leading to the destruction of the alveolar bone, which is essential for supporting the teeth.
But unlike in adults, during the infant stage, that is, during the growth stage, the periodontium is constantly changing due to exfoliation and the eruption of teeth. In fact, in the case of young people, this periodontal disease can present two variants:
- Aggressive, localised periodontitis, which usually affects mainly molars and incisors and is characterised by severe alveolar bone loss. Patients suffering from this type of periodontitis do not usually present large bacterial plaque formations.
- Aggressive and generalised periodontitis affects the whole mouth and is particularly prevalent around puberty, i.e. it is related to the various hormonal changes. In these cases, periodontal disease is usually accompanied by a significant presence of plaque.
It should be remembered that in the growth stage it is essential to maintain the stability and health of the gums and teeth, as the milk teeth that precede the permanent teeth have important functions in the development of the oral cavity. Periodontitis can seriously alter this stability. Hence the importance of knowing what causes periodontitis to appear.
2. Why does periodontitis appear?
What is the origin of periodontitis? What causes the formation of bacterial plaque? How does it reach this state of infection? Generally, the answer to this question is poor oral hygiene, but there may be other important causes to consider, so let’s look at them all in more detail:
- Poor oral hygiene. Periodontal disease is usually caused directly by the accumulation of bacterial plaque, a sticky film made up of bacteria that forms between the teeth and gums. In the presence of food debris, these bacteria can proliferate and, over time, form calculus or tartar that serves as further protection for the bacteria. Therefore, if proper hygiene is not carried out, it is possible to encourage the growth of these bacteria, which are the main cause of the appearance of periodontal diseases and caries.
- Poorly performed orthodontic treatment. Although it is no longer common, you may have heard people around you say that when they had orthodontic treatment as teenagers, they experienced gingivitis. This is due to poor planning and monitoring of the process, caused by too abrupt dental movements. Hence the importance of going to clinics with more experience in orthodontic treatment for children and adolescents.
- Hormonal changes. As we have already mentioned, there is a type of periodontitis that is more prevalent during puberty. During this stage, with the hormonal changes that occur, the inflammatory response of the gums to the presence of bacterial plaque can be altered. For this reason, there is a greater risk of adolescents contracting periodontitis during puberty.
This is why parents should pay special attention to the changes that occur in the teeth and gums of both children and adolescents. Especially if symptoms associated with periodontal disease are detected.
3. How can we detect it in children?
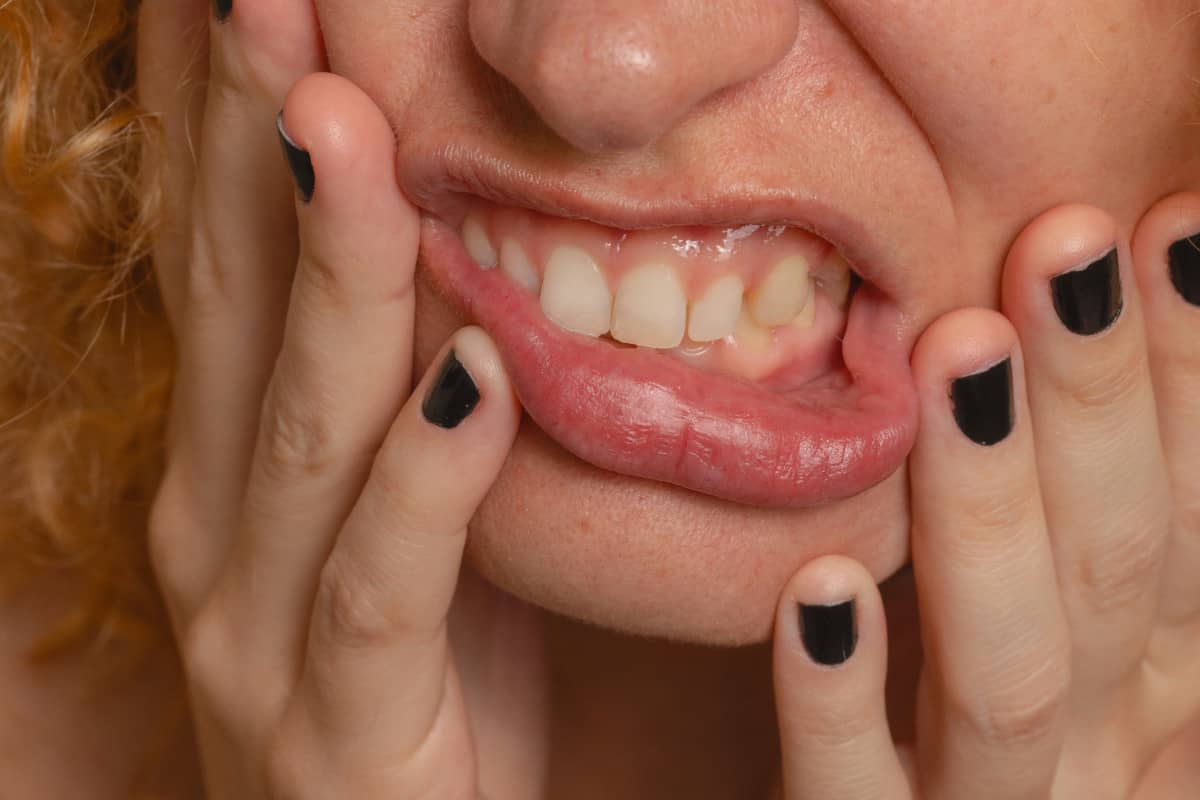
As in adults, the manifestation of a periodontal problem lies in a series of key symptoms to watch out for, especially in younger children, while monitoring for proper oral health and hygiene:
- Bleeding: which can occur both spontaneously at mealtimes, especially if you bite into food that gets into the gums, and during brushing, which is important to spend time on, while being gentle.
- Inflammation of the gums: from mild to more noticeable swelling of the gums, which can also lead to other signs such as increased sensitivity to various foods.
- Redness: generally, healthy gums are pinkish in colour, but with periodontal disease they can become redder, sometimes purplish, a colour change also related to inflammation.
- Bad breath or halitosis: this is also a direct consequence of poor oral hygiene and the decomposition of food in the oral cavity, where bacteria are proliferating.
4. Can childhood periodontitis be prevented?
To prevent the appearance of periodontitis in children, the main cause, the accumulation of bacterial plaque on the teeth, must be avoided. To do this, there are two fundamental habits to take into account, involving both parents and children:
- Teaching good oral hygiene habits. Proper hygiene is key to maintaining the health of teeth and gums, a habit that should be instilled in children from the time they are babies. On the one hand, it is important to teach by example. On the other hand, it is also important to supervise their hygiene once they are acquiring autonomy and explain its relevance to their health. It is also important to be aware of the symptoms mentioned above, although they will not always be evident, which is why it is necessary:
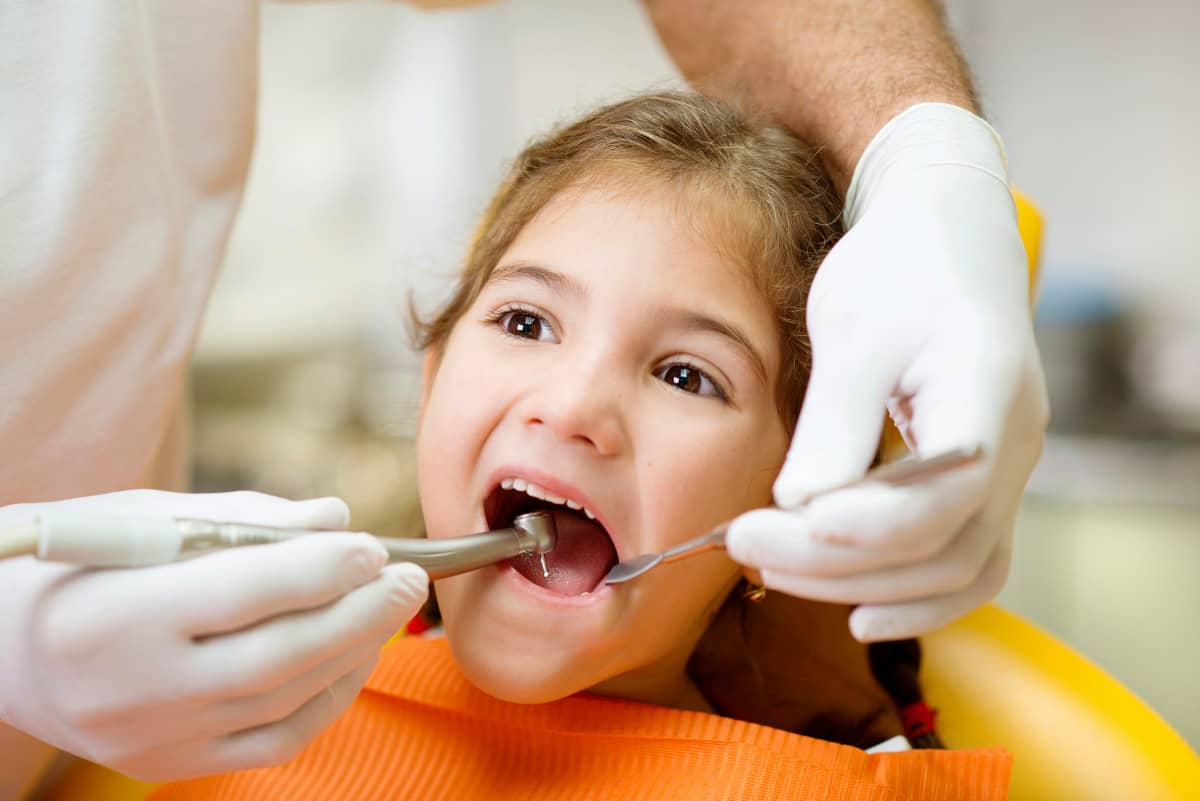
- Regular visits to the paediatric dentist. Only regular check-ups with specialists who have the right diagnostic tools can determine exactly what the state of health of teeth and gums is. Periodontal disease as well as other oral conditions are usually related to the accumulation of bacteria and in practically all cases, simple measures such as dental prophylaxis at the dentist’s office can prevent them.
5. What is periodontal treatment like?
If unfortunately this disease has not been prevented and an early diagnosis has not been made, although the integrity of the teeth and gums may have been affected, there is a treatment to restore periodontal health in the youngest members of the household that consists in carrying out:
- A probing to check the position of the bone and gums. When the presence of periodontal pockets is suspected, it is necessary to verify how seriously the disease has affected the bone and gums. This is done by periodontal probing.
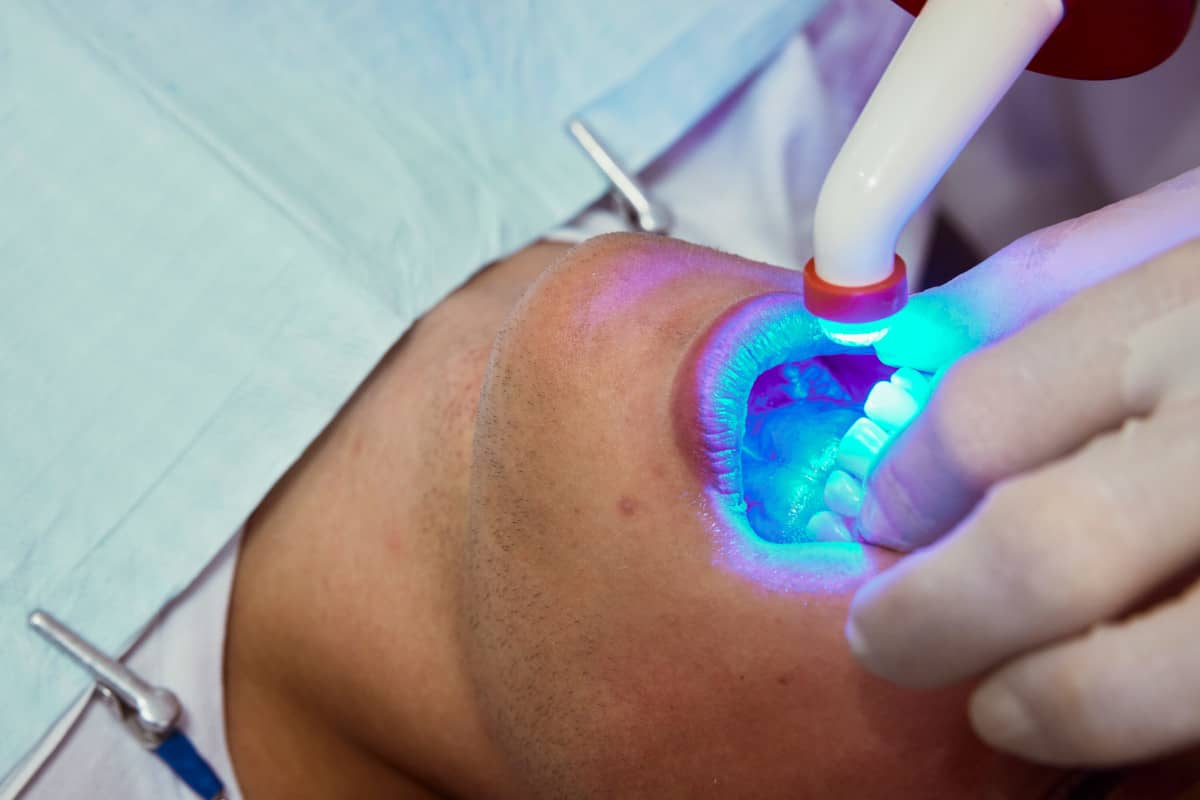
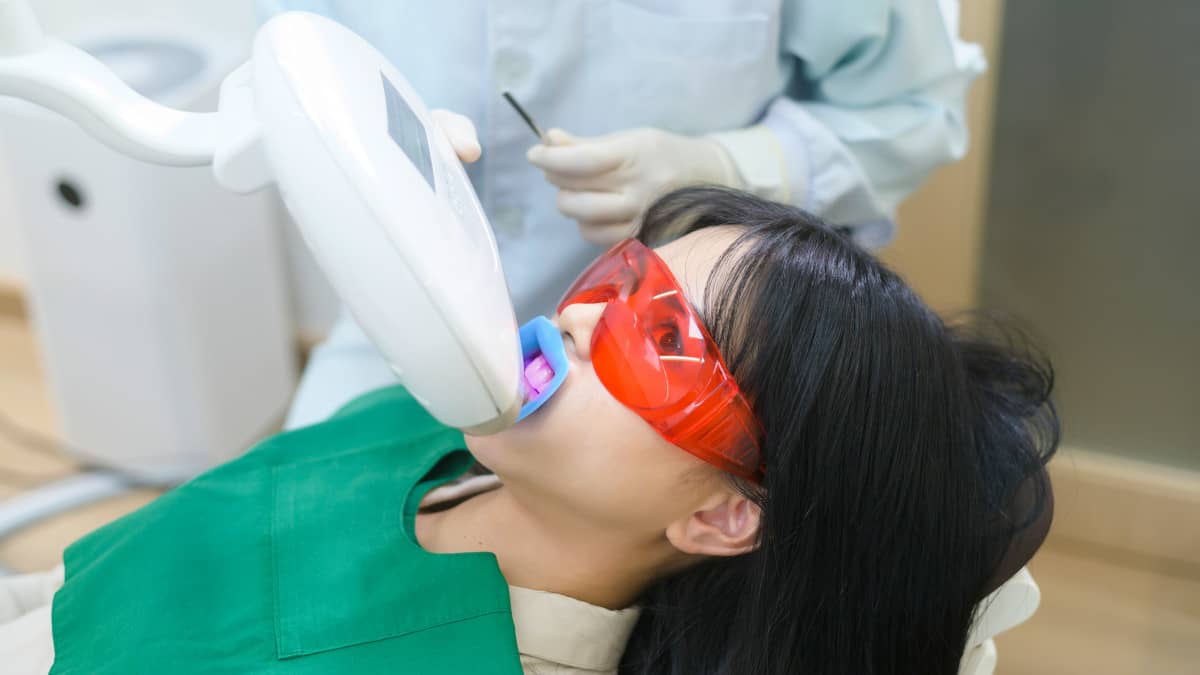
- A dental curettage or scaling and root planing. This procedure is carried out by the periodontist and is performed under local anaesthesia (or, if requested, conscious sedation). The aim of this technique is to remove tartar that has spread to the inside of the gums. After the dental curettage, if deemed necessary, the specialist can proceed with the application of fluoride to improve the resistance of the enamel to the incidence of bacteria.
- Maintenance of the treatment. It is important that this type of infection does not recur. Therefore, in order to maintain healthy gums and teeth, it is essential to continue attending the indicated maintenance sessions.